How many websites are made everyday? Any ideas?
Well, 547,200 websites are made everyday! This covers normal website or blogs. That comes out to 6 websites every second.

This makes it kind of tough to stand out. But you have to if you want to make your website or blog a successful one. Making a website is one part of the web development and the other which is the most important, is optimizing the website pages and blog posts.
On any given day, people conduct more than 2.2 million searches. And that’s just on Google — to say nothing of the other search engines. Therefore, showing up on the front page of Google can be the deciding factor between a business that’s thriving and one that’s, well, will soon be out of business.
But what does SEO even mean? You probably know that it stands for search engine optimization, but what do you need to optimize?
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is a technical, analytical and creative process to improve the visibility of a website in search engines. The primary function of SEO is to drive more unpaid (also known as “organic”) useful traffic to a site that converts into sales. In other words, it is the process of optimizing your online content so that a search engine likes to show it as a top result for searches of a certain keyword or phrase. Paid links have the phrase Ad beside them.
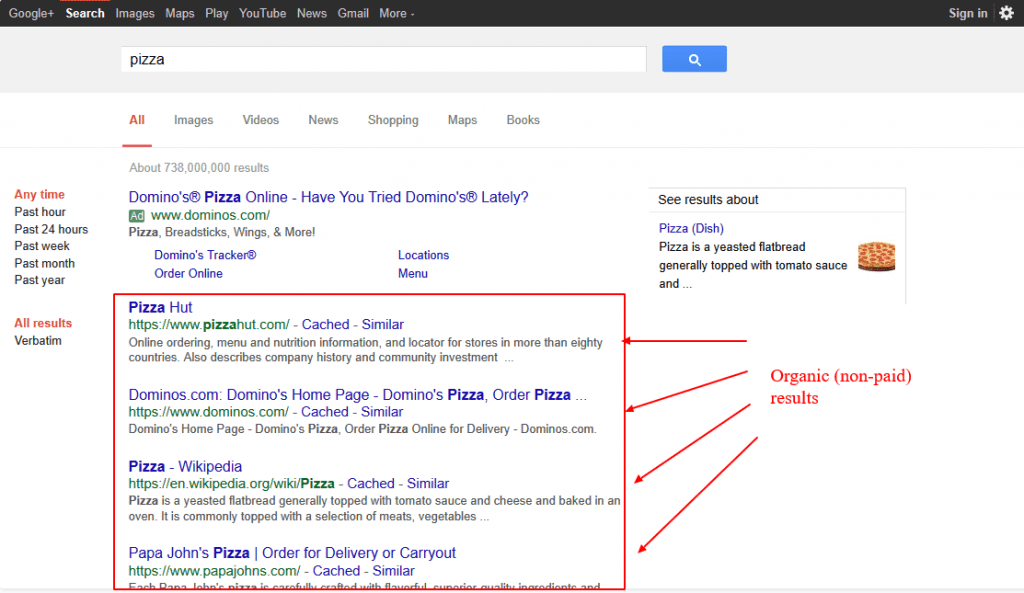
Despite the acronym, SEO is as much about people as it is about search engines themselves. It’s about understanding what people are searching for online, the answers they are seeking, the words they’re using, and the type of content they wish to consume. Knowing the answers to these questions will allow you to connect to the people who are searching online for the solutions you offer.
If knowing your audience’s intent is one side of the SEO coin, delivering it in a way search engine crawlers can find and understand is the other. In this guide, you will learn on how to deliver your website in a way that search engines can find it (On-page SEO).
You can use the table of contents below to jump over to any section.
Basic terms vocabulary:
- On-page vs. off-page SEO
- White hat vs. black hat vs. grey hat SEO
On-page vs. Off-page SEO
Doing On-page (on-site) SEO means optimizing your website to affect search engines results. It’s everything you can do on the website – from content through technical aspects to design:
- meta tags
- headings
- URL structure
- images optimization
- content
- website size and speed
Off-page (off-site) SEO covers all activities you do to improve the domain authority through getting backlinks from other websites. There are many ways to get them:
- exchanging backlinks
- guest blogging
- buying backlinks
- social media efforts
- cooperation with influencers
- writing valuable content, so people would love to link to your website
White hat vs. black hat vs. grey hat SEO
Black hat SEO is a set of unethical practices to improve rankings of a website in the search engine results page. They are designed to affect search engines while not taking human factor into consideration.
Black hat SEO can get you to the top of SERP in a short time, however, search engines will most probably penalize and ban the website sooner or later.
Lists of violating practices can be found in Google’s Webmaster Guidelines or Bing’s Webmaster Guidelines.
White hat SEO is a set of ethical techniques sticking to the guidelines and rules. The basic parts of white hat SEO are:
- quality and relevant content
- link building
White hat SEO is a long-term strategy oriented to customer experience. Being a good guy in the world of SEO should be the proper direction.
Search engines
In this section you will learn how search engines work, how people use them and what type of search queries they submit. Take a look at the technical background behind Google.
How search engines work
Search engines consist of three main ingredients:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Picking the results
The process looks like this:
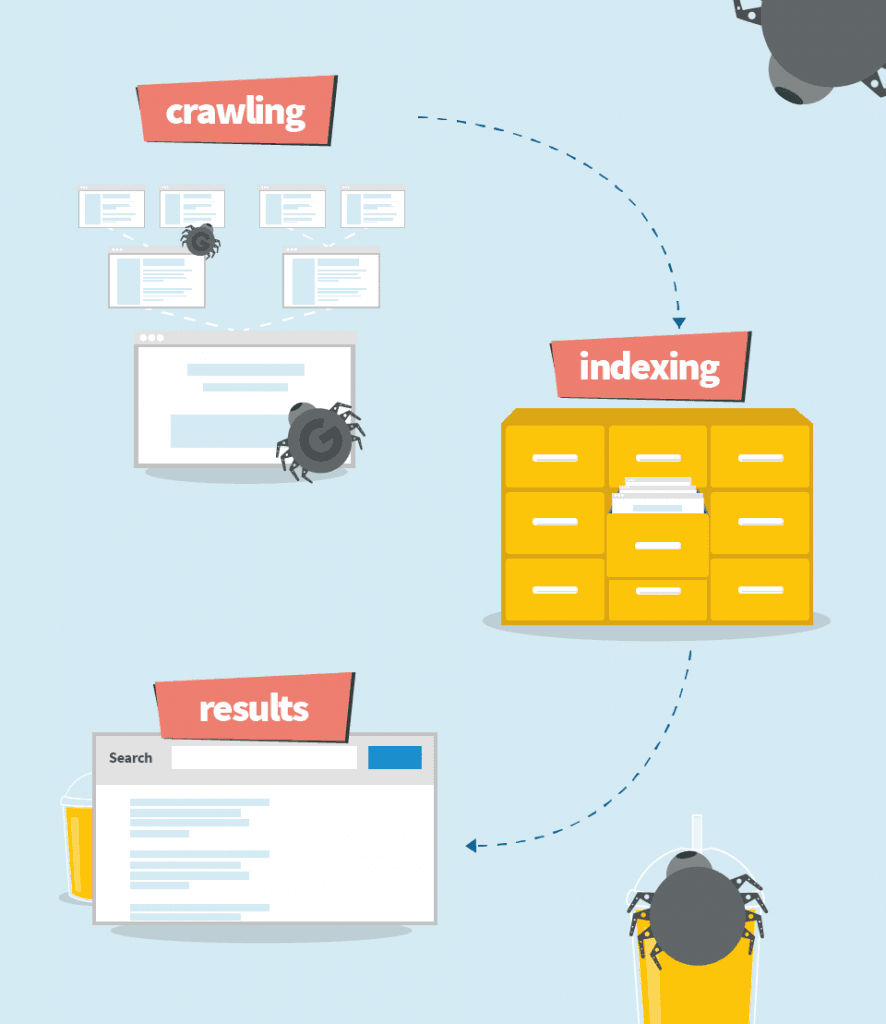
Crawling
Crawling or spidering means scanning the website, its sections, content, keywords, headings, links, images by thousands of small bots. Any data that can be found on the website is crawled.
Crawlers detect any hypertext links on a website pointing to other websites.Then they parse those pages for new links over and over again. Bots crawl the whole internet regularly to update the data.
Indexing
Once the website is crawled, the indexing takes place. Imagine the index as a gigantic catalog or a library full of websites from all over the world. It usually takes some time for a website to be indexed. From our experience, a website can be indexed instantly or from 1 to 10 days.
Picking the results
Results are critical for both developers and users. Once the internet user submits a search query, the search engine digs into the index and pulls out matching results. It’s a process of checking the query against billions of websites based on various algorithms.
Companies running search engines (Google, Microsoft, Yahoo!) keep the exact calculations of their algorithms in secret. Nonetheless, many ranking factors are well-known.
Ranking factors
Most of these factors are proven, but some are just speculations or even myths. On top of that, some are more important than others. Brian Dean from Backlinko made a nice list of Google ranking factors.
You don’t have to know all of them by heart to learn SEO, but it is good to have at least a basic overview.
One of the most important factors, the backlink profile is based on the number and quality of backlinks leading to a website. It’s a very simplified view on Google approximation of the website’s authority. Each backlink is an analogy of an academic citation.
These are some of the most important ranking factors (in no particular order):
- Strength and relevancy of backlinks (incoming links to your website)
- Content relevancy and quality
- Engagement metrics such as CTR (click-through rate)
- Website size and loading speed
- Keyword density, keyword usage in headings, meta tags, URL – these aren’t as important today as they used to be from the technical point of view
- Grammar and spelling
- Website structure
- Mobile optimization
- Overall domain authority
- Social signals
- Internal linking
- Website usability
Ranking factors can be divided into on-page SEO factors (including technical SEO) and link building or off-page SEO factors.
How people use search engines
The main point of SEO is to be friendly both to users and search engines. If you invest all your money and time into perfect technical SEO, it’s fine. But if the user interaction is poor, your positions can suffer. And that’s how you start wasting money. The user’s point of view is a number one priority.
The picture below represents one of the common user journeys in Google search:
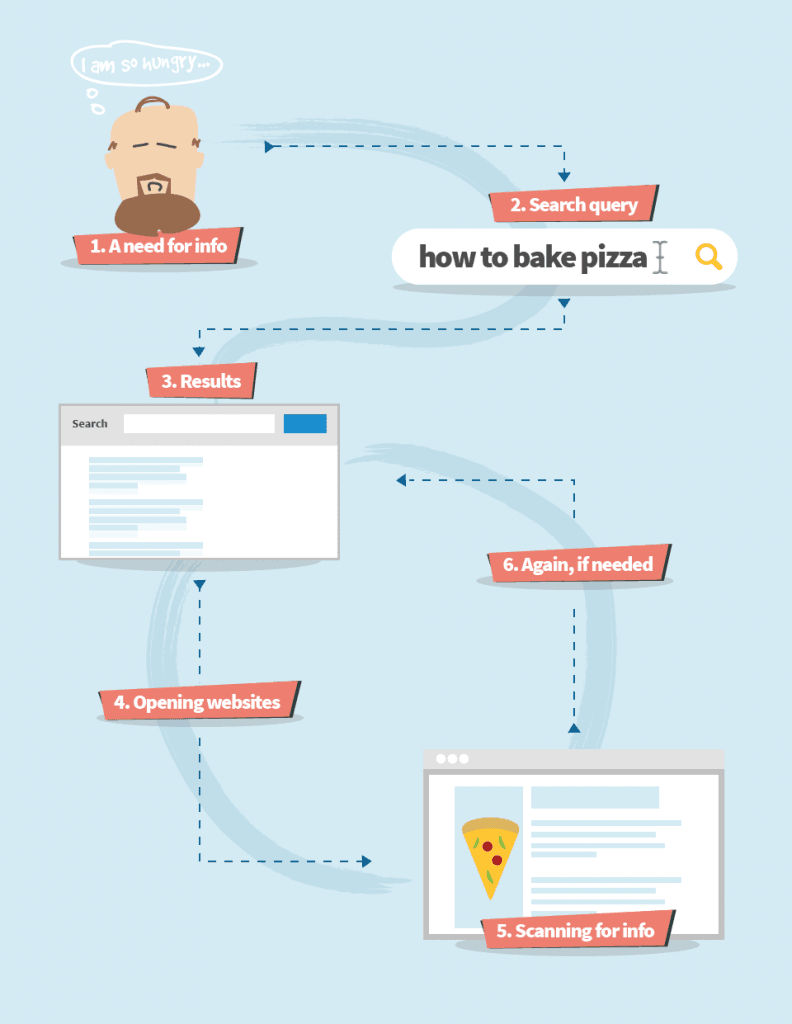
The interactions with search engines have evolved over the years. However, the principle remains the same:
- A need for a solution, information, or an answer
- Typing the need in form of a query (keyword) into the search engine
- Going through the first results
- Clicking on one or more results (websites)
- Scanning websites for the answer
- Going through more results on the 1st SERP and/or changing the search query, if the answer isn’t found.
How do we classify search queries?
There are three generally accepted types of search queries:
- Navigational search queries
- Informational search queries
- Transactional search queries
Navigational search queries
They represent an intent to search for a particular brand or website. People tend to type “youtube” or “google” into search engines rather than using browser’s history or bookmarks.
Informational search queries
These are submitted when users are searching for information. They aren’t looking for a particular website, yet for an answer or guidance on how to do something. For example, “How to bake pizza”.
Transactional search queries
This type is an intention to make a transaction. It usually comes with a product name (Nike Airmax) or category (sneakers). Additionally, it can be written with “Where to buy …”, “… price” or in a similar manner.
1st place vs. 1st page
Being on the first page of the organic search results is good, scoring the top three is great but there’s only one winner, right? Or, is it? It’s a matter of perspective.
Websites all over the world are updated on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. The internet grows every single day. When new websites and changes are indexed by a search engine, the organic results may change.
Another very important factor is Google algorithm which changes all the time. Minor tweaks may not cause anything at all, but a major algorithm update can great effects such as the most recent Google June Core Search Update.
What we’re trying to say is that even if you’re the winner, your positions can (and probably will) be replaced by competitors the other day, and vice versa.
On-page and technical SEO
Meta tags
Meta tags are a part of the HTML code. They describe website’s content. The most important are meta titles and meta descriptions.
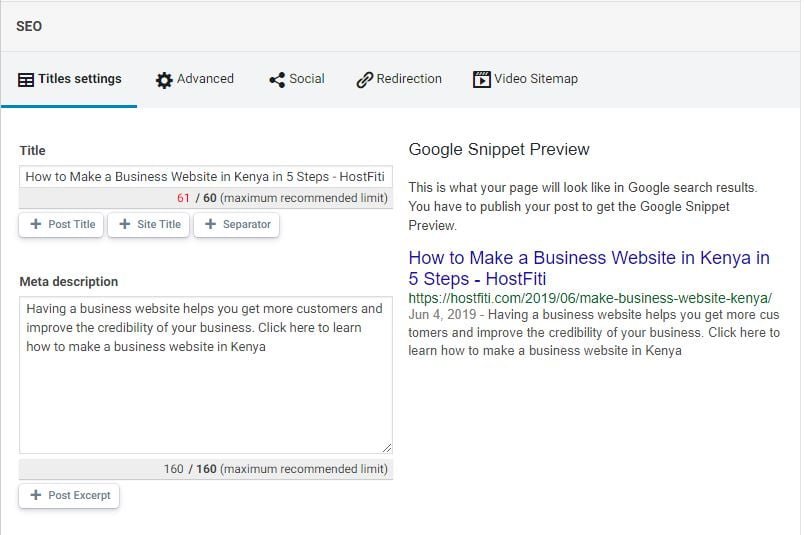
They aren’t as important as they used to be from the technical point of view.
Meta titles and descriptions packed with keywords don’t directly influence your rankings BUT they remain a strong psychological factor affecting the CTR and overall user engagement.
So don’t get confused by blogs saying that title tags and meta descriptions aren’t important at all. On the other hand, keep in mind that Google changes titles and descriptions to better indicate their relevance to the search query in case your text doesn’t match enough.
On-page SEO checklist
Let’s start with the things you can do in HostFiti Website Builder’s interface or in any other content management system.
1. Find out what people are searching before you start writing
Do you plan to write about a topic that people search for? Are you sure your point of view is different, unique? Can you offer new added value to the topic? Is your timing right?
These are the major questions before you start writing and it doesn’t matter whether it’s a blog or a product landing page.
2. Title tags and headlines
Create an appealing title tag, meta description and headlines. Keep in mind what we mentioned earlier. Your main focus keyword should still be there, so users know what is your website about. Use the meta description as a great opportunity for call-to-action (CTA) emphasis.
Persuade both users and search engines that your website is the one to be clicked on.
Once again, think of the user engagement, so don’t overact by using cheap or too cheesy words. Look at your competitors, analyze what works for them and build your own strategy.
Quick tips:
- Google will show the titles if they’re up to 60 characters and meta descriptions up to 160 characters
- Make sure to use correct <h1>, <h2>, <h3>, … structure for good readability and structure. (An example is how this blog post is structured).
- Check the search results preview in tools such as SEOSiteCheckup
3. Use SEO-friendly URLs
Avoid using auto-generated URLs with figures and characters:
www.example.com/2017/post318e7a349f6
Use URLs corresponding to your content and its title:
www.example.com/how-to-bake-pizza
If you make your website using our website builder, we take care of this automatically, so your urls are always SEO friendly.
Some SEO specialists and bloggers say that short URLs ranks better in Google. We think it’s a matter of the user experience. Of course, this doesn’t mean a 20-word URL is alright.
4. Multimedia
Do you want to engage your visitors? Use images, infographics, charts and videos. They lead to lower bounce rates and a higher engagement. Some things have to be written in the good old-fashioned way but multimedia are a must.
Video streaming has been one of the hottest marketing trends over the last couple of years. Furthermore, they motivate people to like, share or comment your content.
Quick tips:
- Optimize images by using relevant file names (how-to-bake-pizza.jpg), alt image attributes and file size
- Embed interactive multimedia such as videos or charts
- Don’t forget to include transcripts so you don’t lose important keywords (the crawlers can’t “read” the video)
5. Outbound and internal links
Using outbound links gives a relevancy signal of your topic to Google. Make sure to link to relevant and authoritative sources.
Internal links are a perfect way to promote your other articles or website sections. It makes easier to visit them and leads to higher engagement. Internal linking also helps the bots to understand the website structure.
Quick tips:
- Outbound links may not directly improve your rankings, yet it is highly advisable to use them
- Use up to 2-3 internal links, depending on the content length
- Search engine crawlers scan these links, so don’t try to cheat and watch out for broken links
Technical on-page SEO checklist
We can classify technical SEO as a part of on-page SEO that deals with more technical stuff. It usually demands development skills or a web developer.
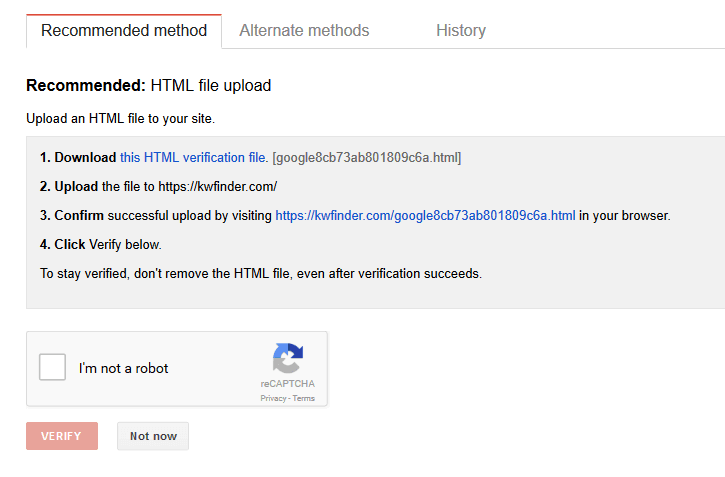
1. Search console
Google Search Console (Webmaster tools) is one of the SEO basics. It helps you to monitor and maintain your site’s presence in Google search results.
That includes content submission for crawling, choosing what you want to be indexed and what not, site errors, structured data or code errors.
The Search Console will help you to analyze your keyword rankings, CTRs, possible Google penalties and many other useful data for technical SEO.
Quick tips:
- Every property (website) needs to be verified to use Search console features
- Connect Search Console with Google Analytics
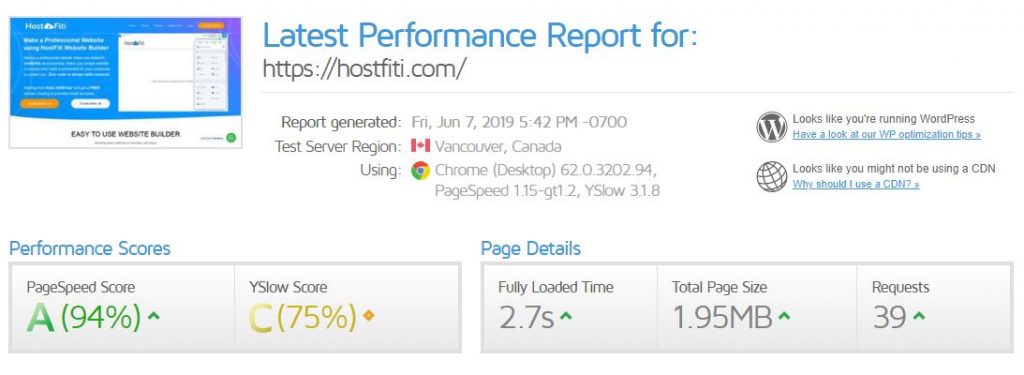
2. Website speed
ebsite speed is one of the ranking factors. Slow website causes that people will leave. It’s known that 50% of web users expect a site to load in 2 seconds or less. If it doesn’t load in 3 seconds, they will leave.
Quick tips:
- Test the speed in PageSpeed Insights
- Optimize images, enable GZIP compression, HTML compression, JS and CSS minification and try to decrease server response time
- Quality web hosting plays a big role in the website speed, so make sure to select a trustworthy provider
3. Mobile optimization
Mobile optimization is a must. The world is shifting from desktop to mobile. In fact, running a website that is not mobile-optimized will negatively influence your rankings.
Google started rolling out the mobile-first indexing in March 2018. Mobile-first indexing means that Google will use the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking.
You can also consider the AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages). AMP is an HTML code extended with custom properties that enable to render static content fast. In 2017, it was one of the main Google’s projects of mobile search. We’ll see if there’s any future for this.
Quick tips:
- Test the responsiveness of your website in the Mobile-Friendly Test
- Monitor your keyword rankings in mobile search results
- Make sure the mobile version of your website works like a charm
4. Sitemap
A sitemap helps search engines to crawl your content. It’s a file where all website sections are listed. It’s good to have one especially when you run a large websitewith a complicated structure or when you use rich media content.
Having a sitemap doesn’t mean your rankings will improve. According to Google, it’s a benefit but you’ll never be penalized for not having one.
Quick tips:
- Not all the websites need a sitemap
- The Sitemap shouldn’t contain more than 50,000 URLs and cannot exceed 50 MB
- Place the sitemap in the root directory of the website:
https://example.com/sitemap.xml
5. Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a file that tells crawlers which website sections you don’t want to be accessed. It’s located in https://example.com/robots.txt and it’s public.
It’s handy when you don’t want some scripts, unnecessary files or images to be indexed.
robots.txt syntax:
User-agent: * (e.g. Googlebot) Disallow: / (e.g. /images/pizza.png)
Quick tips:
- Don’t use robots.txt to hide content from search engines
- Violating or malware robots are able to ignore robots.txt
Conclusion
While it doesn’t take a lot of effort to get a few basics right, it might kill your online presence if you don’t.
Don’t worry if you’ve already made some SEO decisions in the past that might not have been the perfect choices.
Just commit to getting started today.
Do your keyword research before you write your next blog post. Then, use your keyword data to optimize the basics, such as your title tags and descriptions.
And who knows – maybe the next time you press publish, you’ll stand out.
Do you think this article will help someone? Don’t forget to share.
Subscribe to be notified about new marketing, entrepreneurship & web development posts.
Make a Professional Website using HostFiti Website Builder
Having a professional business website helps you establish credibility as a business. Make your professional website using our drag and drop website builder in minutes and make it convenient for your customers to contact you.
Starting from